Linux Device Drivers / System Software Development - 6 month
A Project based Training Program: (6 months):
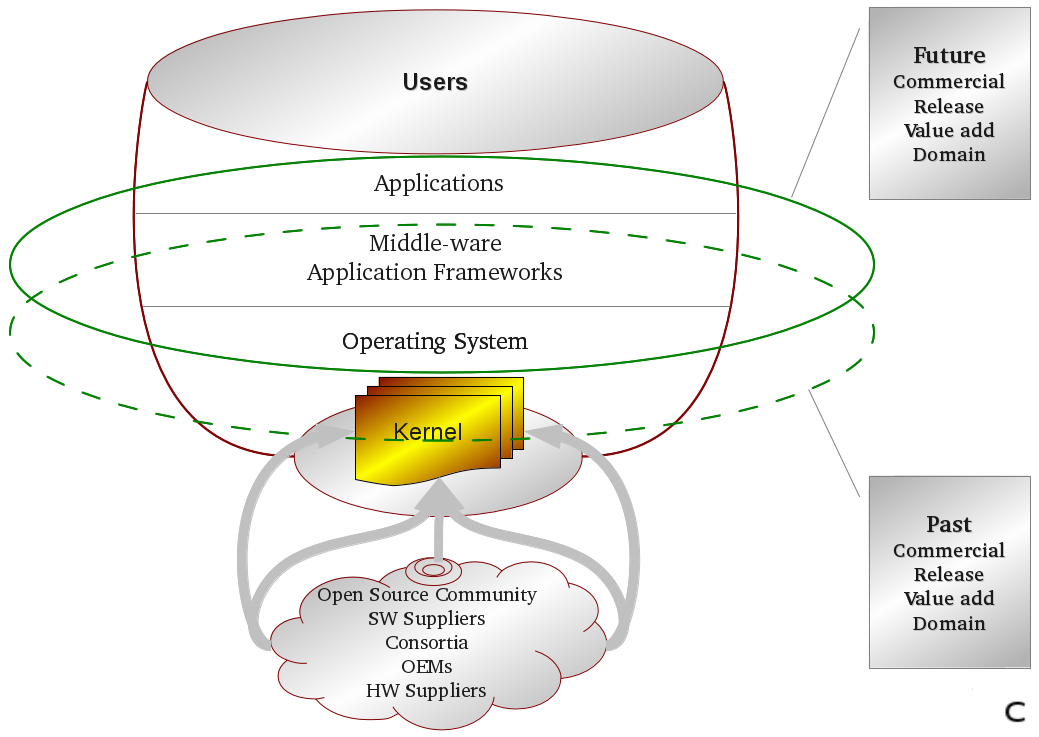 "Linux Device Drivers / System Software Development" is an Ineffable, Comprehensive, Hands-on, project based career oriented, training program for BE, B Tech, ME, M Tech from the streams of Electronics, Computer Science, Information Technologies, Instrumentation or Master of Computer Applications. This trainig aims at building your career with respect to innovative technologies related to Embedded Linux, ARM, Device Drivers, System Software, System Engineering.
"Linux Device Drivers / System Software Development" is an Ineffable, Comprehensive, Hands-on, project based career oriented, training program for BE, B Tech, ME, M Tech from the streams of Electronics, Computer Science, Information Technologies, Instrumentation or Master of Computer Applications. This trainig aims at building your career with respect to innovative technologies related to Embedded Linux, ARM, Device Drivers, System Software, System Engineering.
Training Objective:
The course considers programming techniques which can help to ensure that single-processor embedded systems are reliable.
Pre-requisite:
-
The candidate should be already persuing any of the Following programs:-
- BE, B Tech in Computer Science, Electronics, Information Technology, instrumentation.
- ME, M Tech in Computer Science, Electronics, Information Technology, instrumentation or MCA.
Silent Features of The Program:

-
The Duration of Training should be:(approx)
- 15 weeks.
- There would be 70 Classroom Sessions of 2 Hours each.
- There would be 700 Lab Sessions of 4 hours each.
-
Training Methodology:
- Hands on approach to training, behaviorial model of training would be practiced.
- During the training, the Trainee whould implement 7 different sub-projects related to various modules.
- Comitment to Individual growth and constant evaluation.
-
Deliverables:
-
- use the concept absorbed in the real world situation.
- implement knowledge absorbed in theiir commercial / live projects.
- The probablity for a head-start to the taiinees career should be higher.
-
EmbLogicTM would issue/provide the following:-
- Project Report for Submitting into their college.
- Project presentaation and demonstration assistance.
- Completed Project (by the trainee).
- Certificate of Completion for the training and Project as mentioned above.
-
Training Modules and Projects (in brief):
|
Sl No |
Project No |
Project Name |
Classes (2 Hrs) |
Labs (2 Hrs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 00 | 5 | 5 | |
| 2. | 01 | 20 | 20 | |
| 3. | 03 | 10 | 10 | |
| 4. | 04 | 5 | 5 | |
| 5. | 05 | 20 | 20 | |
| 6. | 06 | 5 | 5 | |
| 7. | 11 | 5 | 5 | |
|
Total Session |
70 | 70 | ||
|
Total Duration (hours) |
420 | |||
A brief description about "Linux System Software and Device Drivers Development"
The digital revolution now has reached to a stage where we cannot conduct our normal modern daily lives without this technology. Indeed, it is reasonable to say that everyone already owns at least one piece of equipment, which contains a processor; whether it is a phone, a television, an automatic washing machine, an MP3 player, microwave oven or anything such.
The colossal growth of processing and controlling power in small packages has fuelled this digital revolution by boon of embedded systems Software. Embedded systems are basically computer based control systems designed to perform specifically dedicated functions within a set of larger system.
Embedded Software System development in India started around early 2000. The market reached approximately $5 billion by 2009 and now has the potential to triple in size by 2015. According to recently released NASSCOM report, the total addressable embedded software system R&D global opportunity is expected to reach approx. $89 billion by 2015 where India alone could contribute approx. $15 billion in size.
Presently many Indian companies provide high level software designs and board level designs in a few cases. Not much work is carried out in terms of application design engineering, hardware design and innovation towards customized product development. This lack of domain expertise in industry is basic impediment for future growth.
-
BIOS: basic input/output system, the built-in software that determines what a system can do without accessing programs from a disk. On PCs, the BIOS contains all the code required to control the keyboard, display screen, disk drives, serial communications, and a number of miscellaneous functions.
-
EFIs: The EFI specification is primarily intended for the IA-32 and Itanium architecture-based computers. The EFI specification defines a model for the interface between operating systems and platform firmware. The interface consists of data tables that contain platform-related information, plus boot and runtime service calls that are available to the operating system and its loader. Together, these provide a standard environment for booting an operating system and running pre-boot applications. EFI is an outgrowth of the "Intel Boot Initiative" (IBI) program that began in 1998.
-
Firmware: Software (programs or data) that has been written onto read-only memory (ROM). Firmware is a combination of software and hardware. ROMs, PROMs and EPROMs that have data or programs recorded on them are firmware.
-
Middleware: Software that connects two separate applications. The term middleware is used to describe separate products that serve as the glue between two applications. Middleware is sometimes called plumbing because it connects two sides of an application and passes data between them.
-
Operating Systems: The operating system is the most important program that runs on a computer. Every computer must have an operating system to run other programs. Operating systems perform basic tasks, such as booting the system, recognizing inputs, sending outputs, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers.
-
Device Drivers: A program that controls a device. Every device, must have a driver program. The driver, accepts generic commands from a program and then translates them into specialized commands for the device. It is an interface between Device and the applications.
-
BootLoader: A small program that loads the operating system into the computers memory when the system is booted and also starts the operating system.
-
MBR: Master Boot Record, a small program that is executed when a computer boots up. Typically, the MBR resides on the first sector of the hard disk. The program begins the boot process by looking up the partition table to determine which partition to use for booting. It then transfers program control to the boot sector of that partition, which continues the boot process.
-
Loaders: It is the program that loads the any program from secondary storage to the Memory
-
Schedulers: It is a program that allocates and deallocates the processor to the running processes.
-
Resource Allocators: It is a program that allocates and releases the resources to the executing processes.
-
Compilers: A program that translates source code into object code.
-
Interpreters: A program that translates a high-level language into machine language by a compiler or interpreter.
-
Assemblers: A program that translates programs from assembly language to machine language.
-
Linkers: Also called link editor and binder, a linker is a program that combines object modules to form an executable program.
-
Debugger: A special program used to find errors (bugs) in other programs. A debugger allows a programmer to stop a program at any point and examine and change the values of variables.
-
Defragmentors: The Disk Defragmenter optimizes the disk by unfragmenting the stored files. The application will locate fragments of files stored in different locations on the disk and then copy them into a single continuous file at a point on the disk that has enough free space.
-
Memory Management Units: Short for memory management unit, the hardware component that manages virtual memory systems. Typically, the MMU is part of the CPU, though in some designs it is a separate chip. The MMU includes a small amount of memory that holds a table matching virtual addresses to physical addresses.
-
Codecs: Short for compressor/decompressor, a codec is any technology for compressing and decompressing data. Codecs can be implemented in software, hardware, or a combination of both.
-
Project Management Tools: Thes are set of software based tools used for Project Management.
Training Modules and Projects in "Linux System Software and Device Drivers Development" (in detail): read more...
EmbLogicTM is an ISO 9001:2008(QMS) (Quality Management System) Certified Company
